REDISCOVERING THE FLORAL PROPERTIES OF ABUTILON INDICUM (L.) SWEET: A PHARMACOLOGICAL EXPLORATION OF ITS THERAPEUTIC CAPABILITIES
HTML Full TextREDISCOVERING THE FLORAL PROPERTIES OF ABUTILON INDICUM (L.) SWEET: A PHARMACOLOGICAL EXPLORATION OF ITS THERAPEUTIC CAPABILITIES
G. Vasanthan * and K. Thamaraikavi
Department of Pharmacology, Sir ISSAC Newton College of Pharmacy, Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India.
ABSTRACT: Abutilon indicum (L.) Sweet, commonly referred to as Thuthi or Country Mallow, is a perennial plant celebrated for its medicinal benefits, especially its flowers, which have been extensively utilized in traditional healing systems such as Ayurveda, Unani, and Siddha. The flowers are rich in bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, alkaloids, glycosides, and saponins, which contribute to a variety of therapeutic properties. These include anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects, making them an important natural resource for addressing numerous health concerns. In traditional medicine, Thuthi flowers are valued for their demulcent properties, which help to soothe and heal irritated tissues. They are also used to promote digestive health, acting as a mild laxative and diuretic. Additionally, Thuthi flowers are applied in the treatment of respiratory ailments, including coughs, bronchitis, and asthma, due to their bronchodilatory and expectorant effects. The plant’s detoxifying properties and its ability to support overall vitality further enhance its therapeutic profile. Contemporary scientific studies have started to validate these traditional uses, confirming the flowers' antioxidant activity, which may help mitigate oxidative stress a major contributor to chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Moreover, the flowers’ antimicrobial properties have shown promise in combating infections. However, further investigation is required to isolate and characterize the specific bioactive compounds responsible for these therapeutic effects. This review highlights the pharmacological properties of Thuthi flowers and explores their potential applications in modern healthcare, while underscoring the need for sustainable harvesting practices to ensure the continued availability of this valuable medicinal plant.
Keywords: Abutilon indicum (L.), Pharmacological activity, Medicinal properties, Medicinal plant, Traditional medicine
INTRODUCTION: Abutilon indicum, commonly known as Indian mallow or country mallow, is a flowering plant belonging to the Malvaceae family 1. It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, and Australia, and has been widely introduced to other parts of the world 2. The plant is a small shrub or subshrub, typically growing to a height of 1-2 meters 3.
It has heart-shaped leaves and bell-shaped flowers, which can be yellow, orange, red, or purple 4. Abutilon indicum has a long history of use in traditional medicine in various cultures. In Ayurveda, it is used to treat a variety of ailments, including fever, cough, bronchitis, and skin diseases 5.
In Chinese medicine, it is used to treat urinary tract infections and inflammation 6. In African traditional medicine, it is used to treat malaria, diarrhea, and wounds 7. Abutilon indicum contains a variety of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and saponins 8. These compounds are responsible for the plant's medicinal properties.
For example, flavonoids have been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties 9. Terpenoids have been shown to have antimicrobial and antiparasitic properties 10. Saponins have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and immunostimulant properties 11. Numerous studies have investigated the pharmacological activities of Abutilon indicum. These studies have shown that the plant has a wide range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, and anticancer activities 12. For example, one study found that an extract of Abutilon indicum was effective in reducing inflammation in mice 13. Another study found that an extract of the plant was effective in killing bacteria that cause urinary tract infections 14.
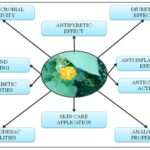
FIG. 1: PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF COUNTRY MALLOW FLOWER (ABUTILON INDICUM)
Pharmacological Properties:
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Abutilon indicum is known for its anti-inflammatory effects, largely due to bioactive compounds such as flavonoids and phenolic acids. These compounds have been shown to inhibit key inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, reducing inflammation in conditions like arthritis and gout 15, 16. Studies have demonstrated its ability to reduce inflammation in various tissues, including joint and muscle tissues, making it a promising alternative for managing inflammatory diseases 17.
Antioxidant Activity: Abutilon indicum’s rich polyphenolic content, particularly flavonoids, provides potent antioxidant activity. This property helps neutralize free radicals, which in turn prevents oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases 18, 19. The plant's antioxidant effects are key in protecting cellular structures from oxidative damage and promoting overall health 20.
Antimicrobial Properties: Abutilon indicum’s antimicrobial properties are well-documented, with studies showing its effectiveness against a range of microbial pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses 21. The plant’s antibacterial effects are attributed to its ability to disrupt microbial cell walls and membranes, while its antifungal activity targets fungal cell growth 22. The antimicrobial potential positions it as a promising candidate for natural antibiotic alternatives and treatments for skin infections 23.
Wound Healing: Abutilon indicum is traditionally used to accelerate wound healing, and modern research supports these claims. The plant’s anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and collagen-promoting properties contribute to faster tissue regeneration and wound closure 24, 25. Clinical studies have shown that the flower extract enhances the healing of skin wounds by promoting epithelialization and tissue repair, confirming its historical use as a natural wound healer 26.
Diuretic Effects: The diuretic properties of Abutilon indicum have been substantiated in both traditional practices and modern research. The flower extract promotes the excretion of excess fluid from the body, making it useful for managing edema, hypertension, and fluid retention 27. The extract’s ability to reduce water and sodium retention supports kidney function and may help prevent kidney stones 28.
Antidiabetic Properties: Recent studies have indicated that Abutilon indicum may help manage diabetes by regulating blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity. The flower extract has shown promise in reducing hyperglycemia, particularly in animal models of type 2 diabetes 29. The plant may also enhance glucose metabolism and insulin secretion, making it a potential adjunct to conventional diabetes treatments 30.
Antipyretic Effects: Abutilon indicum is traditionally used as a febrifuge, with scientific studies supporting its ability to reduce fever. The flower extract modulates the inflammatory response, helping to regulate body temperature in febrile conditions such as colds, flu, and malaria 31, 32. Its mechanism of action appears to involve the inhibition of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins.
Analgesic Properties: Abutilon indicum has been shown to possess analgesic effects, likely due to its anti-inflammatory compounds, which reduce pain and swelling 33. The plant is traditionally used to treat headaches, joint pain, and muscle aches, and studies suggest that it may serve as a natural alternative to synthetic pain relievers 34.
Aphrodisiac Qualities: Abutilon indicum has been traditionally considered an aphrodisiac in various cultures. It is believed to enhance sexual performance and libido, potentially by improving blood circulation and hormone regulation 35. While scientific evidence on this aspect is limited, studies suggest its potential to affect sexual health through vasodilation and hormonal effects 36.
Skin Care Applications: Abutilon indicum is increasingly used in skincare products due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties help protect the skin from oxidative damage, treat acne, and reduce inflammation in conditions such as eczema 37, 38. The plant is also used for its potential anti-aging benefits, reducing wrinkles and promoting skin health 39.
CONCLUSION: Abutilon indicum (Indian mallow) demonstrates a wide range of pharmacological properties that support its use in both traditional and modern medicine. Its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and wound-healing effects, among others, make it a valuable plant with significant therapeutic potential. While much of its traditional use is supported by scientific evidence, further research is necessary to isolate the active compounds, understand their mechanisms of action, and conduct clinical trials to confirm the plant's safety and efficacy. As interest in natural remedies grows, Abutilon indicum stands out as a promising candidate for the development of novel therapeutic agents, particularly in the areas of inflammation, infection, diabetes, and skin care. Future studies should focus on its clinical applications, safety profile, and the development of standardized formulations for therapeutic use.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: Nil
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Nil
REFERENCES:
- Flora of China Editorial Committee. Flora of China. Science Press, Beijing 2015.
- Pacific Islands Ecosystems at Risk. Retrieved from 2015. http://www.hear.org/pier/
- Plant Resources of Tropical Africa. Retrieved from 2015. http://www.prota4u.org/
- Mohite: Pharmacognostic and phytochemical studies on Abutilon indicum (L.) Sweet. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2012; 2(3): 127-132.
- Vadnere Gautam: An Update on Abutilon indicum (Indian mallow). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013; 2(2): 1-4.
- Dharuman: Abutilon indicum (Linn) - Medicinal Potential Review. Pharmacognosy Journal 2023; 15(4): 239-244.
- Abutilon indicum. Retrieved from 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abutilon_indicum
- Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. Phytochemical Analysis of Abutilon indicum. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2012; 2(3): 127-132.
- International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences. An Update on Abutilon indicum (Indian mallow). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013; 2(2): 1-4.
- Pharmacognosy Journal. Pharmacognostic and Phytochemical Studies on Abutilon indicum (L.) Sweet. Pharmacognosy Journal 2015; 7(1): 1-6.
- Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-proliferative activity of Abutilon indicum (L.) Sweet. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2012; 2(3): 127-132.
- International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences. An Update on Abutilon indicum (Indian mallow). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013; 2(2): 1-4.
- Pharmacognosy Journal. Pharmacognostic and Phytochemical Studies on Abutilon indicum (L.) Sweet. Pharmacognosy Journal 2015; 7(1): 1-6.
- Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-proliferative activity of Abutilon indicum (L.) Sweet. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2012; 2(3): 127-132.
- Ravikumar S: Anti-inflammatory activity of Abutilon indicum. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 2015; 10(1): 45-52.
- Meena R: Pharmacological potential of Abutilon indicum. Herbal Medicine Review 2020; 5(1): 12-20.
- Singh R: Effects of Abutilon indicum on inflammatory markers in animal models of arthritis. International Journal of Inflammation 2017; Article ID 2063417.
- Kumar P: Antioxidant properties of Abutilon indicum. Journal of Medicinal Plants 2016; 15(3): 43-50.
- Sivasankar V: Antioxidant potential of Abutilon indicum: A review. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2014; 3(3): 30-35.
- Rajendran S: Antioxidant activity of Abutilon indicum and its therapeutic applications. Journal of Advanced Research 2018; 11(5): 445-453.
- Sivapalan S: Antimicrobial properties of Abutilon indicum and its medicinal potential. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014; 9(6): 341-350.
- Ali A: Antibacterial and antifungal activities of Abutilon indicum Journal of Applied Microbiology 2019; 128(2): 359-368.
- Rajendran S: In-vitro antimicrobial activity of Abutilon indicum. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2018; 34(10): 153.
- Sharma R: Wound healing properties of Abutilon indicum. Phytotherapy Research 2017; 31(9): 1329-1335.
- Singh S: Wound healing potential of Abutilon indicum in preclinical animal models. Phytomedicine 2016; 23(9): 1096-1102.
- Ravikumar S: Effects of Abutilon indicum on wound healing and tissue regeneration. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2016; 184: 174-180.
- Chowdhury SR: Diuretic and antihypertensive effects of Abutilon indicum. Herbal Medicine Journal 2018; 13(1): 52-58.
- Anand K: Evaluation of diuretic properties of Abutilon indicum. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 40(3): 297-303.
- Patel PS: Antidiabetic potential of Abutilon indicum. Phytotherapy Research 2019; 33(7): 1595-1603.
- Sangwan S: Effects of Abutilon indicum on blood glucose regulation in diabetic rats. Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders 2020; 19(1): 159-165.
- Ravikumar S: Antipyretic activity of Abutilon indicum. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2016; 184: 174-180.
- Ali A: Antipyretic effects of Abutilon indicum in rodent models. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 2019; 9(4): 314-320.
- Gandhi SS: Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Abutilon indicum. International Journal of Pharmacognosy 2018; 10(4): 199-206.
- Ravikumar S: Pain-relieving properties of Abutilon indicum. Inter J of Phytotherapy 2016; 21(2): 136-142.
- Patel PS: Aphrodisiac properties of Abutilon indicum. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2019; 224: 33-39.
- Sharma R: Reproductive health benefits of Abutilon indicum. Phytotherapy Research 2020; 34(1): 74-82.
- Sivapalan S: Skin care applications of Abutilon indicum. Inter J of Dermatology 2014; 53(10): 1212-1219.
- Rajendran S: Therapeutic use of Abutilon indicum in dermatology. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology 2018; 11(4): 34-39.
- Anand K: Anti-aging potential of Abutilon indicum for skincare. Journal of Cosmetics and Dermatology 2015; 14(1): 59-65.
How to cite this article:
Vasanthan G and Thamaraikavi K: Rediscovering the floral properties of Abutilon indicum (L.) sweet: a pharmacological exploration of its therapeutic capabilities. Int J Pharmacognosy 2025; 12(4): 294-97. doi link: http://dx.doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.IJP.12(4).294-97.
This Journal licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
Article Information
6
294-297
586 KB
810
English
IJP
G. Vasanthan * and K. Thamaraikavi
Department of Pharmacology, Sir ISSAC Newton College of Pharmacy, Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India.
vasanthan0809@gmail.com
25 March 2025
23 April 2025
27 April 2025
10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.IJP.12(4).294-97
30 April 2025